Barriers to Psychiatric Diagnosis
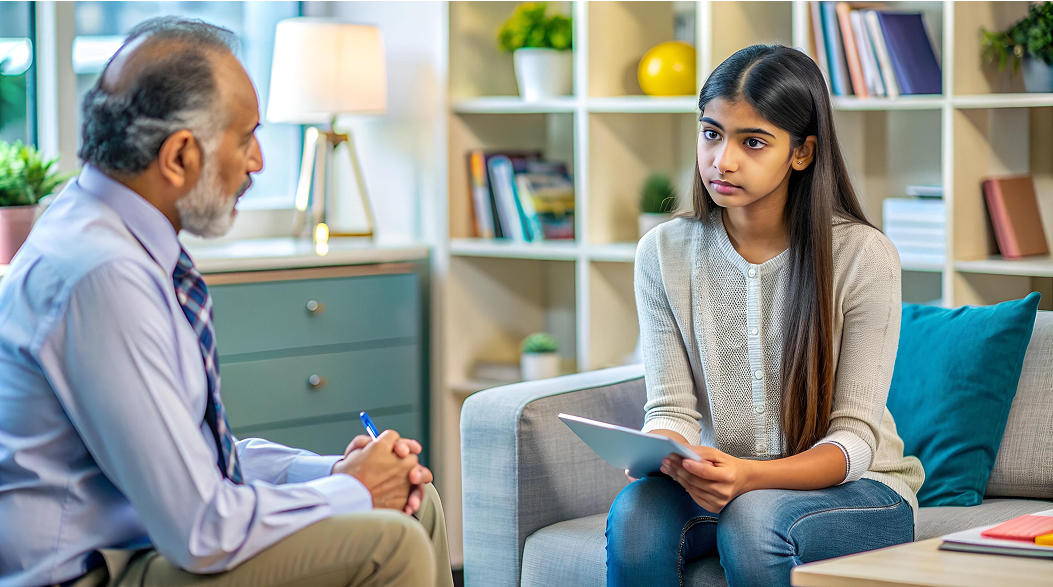
Barriers to psychiatric diagnosis include stigma and social perceptions that discourage individuals from seeking help, symptom overlap among disorders, and comorbidity that complicates accurate identification. Additionally, the lack of standardized diagnostic tools, subjectivity in diagnosis, and cultural factors can impede effective diagnosis, affecting the quality of care and treatment outcomes.

Barriers to accurate psychiatric diagnosis can be multifaceted, stemming from various sources. These obstacles can significantly impact the quality of care and treatment outcomes for patients. Here are some of the key barriers:
Stigma and Social Perceptions
Mental health stigma, both in society and within healthcare settings, can discourage individuals from seeking help or openly discussing their symptoms, leading to underreporting or misrepresentation of symptoms.
Symptom Overlap
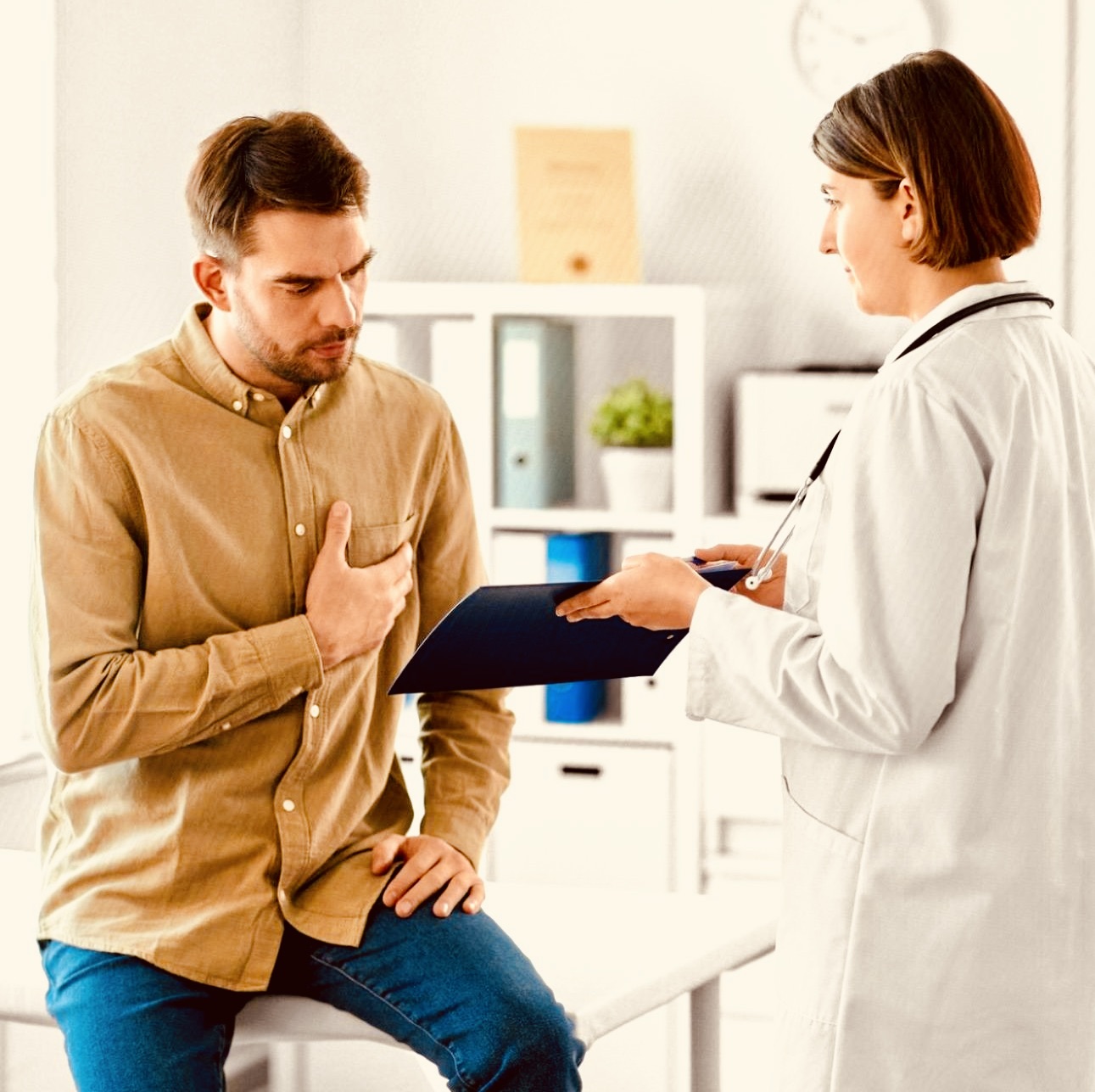
Many psychiatric disorders share similar symptoms, making it challenging to distinguish one disorder from another.
Comorbidity
The presence of multiple disorders in the same individual can complicate the diagnostic process, as symptoms of different disorders can mask or mimic each other.
Subjectivity in Diagnosis
Psychiatric diagnosis often relies heavily on subjective self-reports from patients and clinical judgment, which can vary between practitioners.
Cultural Factors
Cultural differences can influence the presentation and interpretation of psychiatric symptoms. Certain behaviours or feelings might be considered pathological in one culture but not in another.
Limited Access to Qualified Mental Health Professionals
In many regions, there's a shortage of mental health professionals, which can delay diagnosis and treatment.
Resource Constraints
Limited resources, including time during consultations and access to specialized diagnostic tools or referral options, can impede thorough diagnostic evaluations.
Patient Heterogeneity
Individual variations in the presentation of psychiatric disorders can make it difficult to apply standard diagnostic criteria.
Evolution of Diagnostic Criteria
As understanding of psychiatric disorders evolves, diagnostic criteria can change, sometimes leading to confusion or the need for re-evaluation of previous diagnoses.
Healthcare Provider Bias
Personal biases or lack of training in mental health can lead to misdiagnosis or overlooking psychiatric conditions, especially in settings where mental health is not the primary focus.
Communication Barriers
Difficulty in communication, whether due to language differences, cognitive impairments, or young age, can hinder the accurate conveyance and interpretation of symptoms.
Conclusion
Addressing these barriers requires a multifaceted approach, including improving education and training in mental health for healthcare providers, enhancing public awareness and reducing stigma, and developing more robust and culturally sensitive diagnostic tools and procedures.
Try XYCHIATRY today
- See how it works in real-time. Take a quick self-assessment or walk through a sample patient case. No signup required.